Understanding the Importance of Dental Care for Your Overall Wellness
Introduction
Maintaining optimal oral health is not just about having a bright smile. It's a crucial component of your overall well-being.
This comprehensive guide is designed to educate patients on the vital connections between dental care and systemic health. From the risks of periodontal disease and its stages to the implications of poor oral hygiene on conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and even oral cancer, this resource aims to provide clear, actionable information.
This guide was created to help patients understand the importance of regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, and early intervention in preventing serious health issues. By prioritizing your oral health, you can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the risk of various systemic diseases. Let's explore the essential aspects of dental care and its far-reaching impacts on your health.

General Health and Oral Hygiene
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for overall health. Poor oral health leads to chronic inflammation, which is a risk factor for many systemic diseases. Managing conditions like diabetes and heart health is crucial for keeping your mouth healthy and vice versa.
Oral Health and Overall Health
Good oral health can prevent respiratory infections, endocarditis, and complications in diabetes management.
Longevity and Oral Health
Research has shown that there is a significant correlation between the number of teeth and the lifespan of that person. Individuals with more teeth at age 70 tend to live longer than those with fewer teeth. Studies show people with healthy teeth and gums live 7 to 10 year longer that those who don't.
Increase Your Lifespan
This correlation suggests that maintaining good oral health can directly impact overall longevity. Tooth loss can indicate other underlying health problems that might reduce lifespan, making it crucial to preserve oral health.
Systemic Conditions Linked to Oral Health
Periodontal disease and poor oral health are linked to several severe systemic conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, stroke, and certain cancers. Ignoring oral health can lead to life-threatening diseases.
Periodontal Disease
Periodontal Disease is an infection of the gums and the structures supporting the teeth. It is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. If not properly managed, this plaque can harden into tartar, which further irritates the gums and leads to bone loss, which leads to loss of teeth. The disease progresses through several stages.
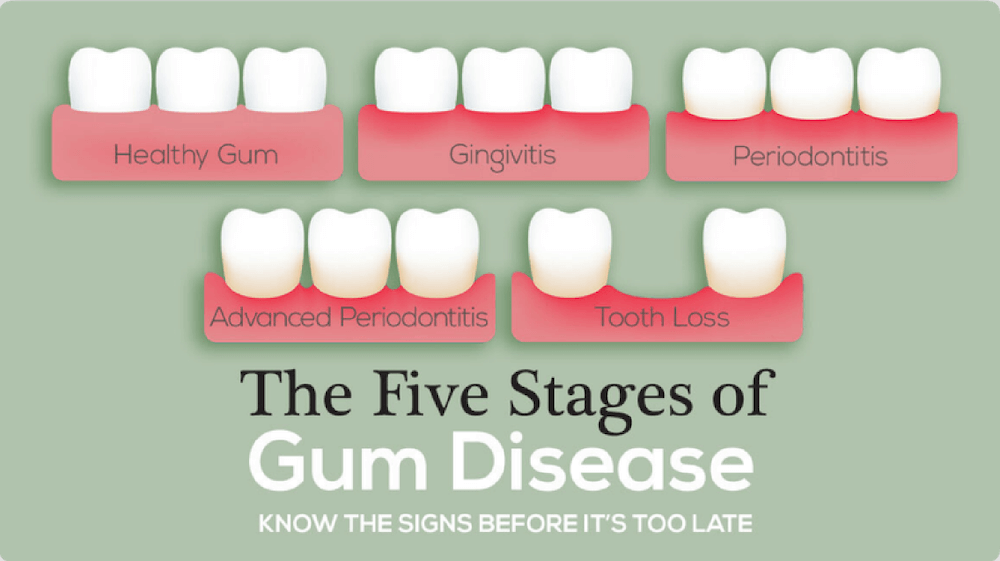
The 5 Stages of Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, progresses through various stages if left untreated. Here are the five stages.
1. Healthy Gums
Description: At this stage, the gums are pink, firm, and securely attached to the teeth. There is no bleeding during brushing or flossing.
How to Maintain Healthy Gums: Good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and cleanings.
2. Gingivitis
Description: The earliest stage of gum disease, characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. Plaque buildup along the gumline causes inflammation.
Symptoms: Red, swollen gums, bleeding when brushing or flossing, bad breath.
Treatment: Improved oral hygiene, in-depth professional dental cleanings, and possibly antibacterial mouthwash.
Sources: American Dental Association, CDC
3. Early Periodontitis
Description: Gingivitis progresses to early periodontitis if not treated. The infection spreads to the bone supporting the teeth, causing slight bone loss.
Symptoms: Increased swelling and redness of gums, bleeding, slight bone loss visible on dental X-rays.
Treatment: Scaling and root planing (deep cleaning), continued good oral hygiene, and possible antibiotic therapy.
Sources: National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research
4. Moderate to Advanced Periodontitis
Description: At this stage, the infection and inflammation cause moderate bone loss and the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums.
Symptoms: Gums may recede, moderate bone loss, deeper pockets around teeth and potential tooth mobility.
Treatment: Scaling and root planing, possible surgical treatments, continued good oral hygiene, and antimicrobial treatments.
Sources: Mayo Clinic
5. Advanced Periodontitis & Tooth Loss
Description: The most severe stage, characterized by significant bone loss, deep pockets, and possible tooth loss. The infection can destroy the bone and connective tissue that support the teeth, and teeth may be lost.
Symptoms: Deep pockets, significant gum recession, loose or shifting teeth, pus between gums and teeth, pain while chewing and even loss of teeth.
Treatment: Advanced periodontal surgery, such as flap surgery or bone and tissue grafts, tooth extraction if necessary, and rigorous oral hygiene practices.
Sources: American Academy of Periodontology, WebMD
Gum Disease: Summary
Causes: Plaque buildup, poor oral hygiene, smoking, certain illnesses (e.g., diabetes), medications that reduce saliva flow, and genetic susceptibility.
Symptoms: Swollen, red, or bleeding gums, bad breath, loose teeth, receding gums, and discomfort while chewing.
Treatment: Professional dental cleaning, improved oral hygiene, medications, and in severe cases, surgical interventions.
Sources: American Dental Association; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research

Heart Disease
People with periodontal disease are at a significantly higher risk of heart disease. Inflammation and bacteria from the mouth can travel through the bloodstream, leading to serious heart-related issues.
Bleeding Gums Linked to Heart Disease
Gum disease can increase the risk of heart disease by allowing bacteria to enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation in the heart.
Tooth Loss and Heart Disease
Losing teeth is associated with a higher risk of heart disease, underscoring the need to maintain oral health for cardiovascular wellbeing.
Endocarditis: Impact of Oral Health on Overall Health
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for preventing chronic inflammation, a known risk factor for many systemic diseases, such as endocarditis.
Endocarditis is the infection of the heart’s inner lining and can occur when bacteria from the mouth spread through the bloodstream and attach to damaged areas in the heart.
Respiratory Infections
Studies have shown that bacteria from periodontal disease can be aspirated into the lungs, leading to respiratory infections such as pneumonia. This is particularly dangerous for elderly individuals and those with compromised immune systems.
Respiratory Conditions
Bacteria from the mouth can be pulled into the lungs, causing pneumonia and other respiratory diseases.
Kidney Disease
Research indicates that individuals with periodontal disease are more likely to develop chronic kidney disease (CKD). Inflammation caused by periodontal disease can exacerbate kidney conditions, potentially leading to severe complications.
Hypertension
Gum disease is associated with higher blood pressure and worse control of hypertension.
Dementia
Tooth loss and gum inflammation have been linked to cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease.
Obesity
Poor oral health has been associated with obesity. Inflammation from periodontal disease can contribute to metabolic changes that promote weight gain. Conversely, obesity can exacerbate periodontal disease, creating a vicious cycle.
Diabetes
Poorly controlled diabetes leads to severe periodontal disease, and severe periodontal disease can worsen diabetes. This bidirectional relationship means that neglecting oral health can make diabetes management more challenging and vice versa.
Oral Health and Diabetes
Gum disease is more frequent and severe among people with diabetes, affecting their ability to control blood sugar levels.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
There is a significant link between periodontal disease and rheumatoid arthritis. Both conditions share common inflammatory pathways, and treating periodontal disease can help alleviate symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
Stroke
Neglecting regular dental care increases the risk of developing a stroke. Poor oral hygiene and periodontal disease lead to higher levels of inflammatory markers, which are associated with an elevated risk of stroke.
Cancer
Poor oral health is linked to an increased risk of various cancers, including liver, pancreatic, and oral cancers.
Poor Oral Health Linked to Liver Cancer
Individuals with poor oral health have a 75% increased risk of developing liver cancer.
Oral Cancer & Dental Health
What is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the tissues of the mouth or throat. It can affect any part of the oral cavity, including the lips, gums, tongue, inner lining of the cheeks, roof of the mouth, and the floor of the mouth. Early signs may include sores, lumps, or rough spots in the mouth, and persistent pain or difficulty swallowing.
How We Can Prevent and Detect Oral Cancer
Taking care of your teeth and gums is crucial not just for preventing cavities and gum disease, but also for reducing the risk of oral cancer. Here's how oral health is tied to oral cancer:
- Early Detection
Regular dental check-ups allow dentists to spot early signs of oral cancer. Dentists can identify abnormal tissues or precancerous conditions, leading to early intervention and treatment.
- Preventing Chronic Inflammation
Poor oral hygiene can lead to chronic inflammation and infections in the mouth. Chronic inflammation has been linked to an increased risk of cancer, including oral cancer.
- Reducing Risk Factors
Good oral hygiene reduces the growth of harmful bacteria and the formation of oral lesions that can become cancerous. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental cleanings help maintain a healthy oral environment.
- Nutritional Health
A healthy mouth supports good nutrition, which is essential for overall health and cancer prevention. Damaged teeth and gums can make eating painful, leading to poor nutrition and increased cancer risk.
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene and regularly visiting the dentist play a vital role in preventing oral cancer. By keeping your mouth healthy, you reduce the risk factors associated with oral cancer and increase the chances of early detection and successful treatment.
Sources: American Cancer Society; Mayo Clinic; National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research

Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes
Periodontal disease during pregnancy is linked to preterm birth and low birth weight. The inflammation and bacteria from gum disease can affect the developing fetus, leading to complications.
Pregnancy Complications
Oral health is crucial during pregnancy. Periodontal disease is linked to low birth weight and preterm births, posing significant risks to both the mother and the baby. Pregnant women with gum disease are at a higher risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes Dental Health.
Dental Procedures and Pregnancy
Proper oral health care and dental procedures during pregnancy can reduce the risk of preterm birth.
Oral Hygiene and Pregnancy
Poor oral hygiene can lead to complications during pregnancy, such as low birth weight and preterm births.
Oral Health and the Common Cold, the Flu, and even COVID
Recent studies highlight the connection between oral health and the severity of COVID. Good oral hygiene can potentially reduce the severity of COVID symptoms by lowering bacterial load and inflammation in the body.
Good oral hygiene can reduce the severity of COVID and other respiratory infections.
Summary
These findings highlight the urgent need for regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene, and early intervention in oral health issues to prevent serious systemic health problems. By understanding these risks, you are encouraged to prioritize your dental health as an integral part of your overall health and wellness strategy.
© 2024 Blumberg Digital. All rights reserved.
